Chances are that you’ve already been warned about gum disease. Most of us are taught the importance of regular dental care at an early age. And yet, 50% of adults in America suffer from gingivitis—an early form of gum disease. Improper care routines can lead to painful and serious side effects and even illness. Identifying periodontal disease symptoms and severe gum disease early is crucial to prevent progression and protect your gum tissue, jaw bone, and overall oral health.
Learn to Recognize Periodontal Disease
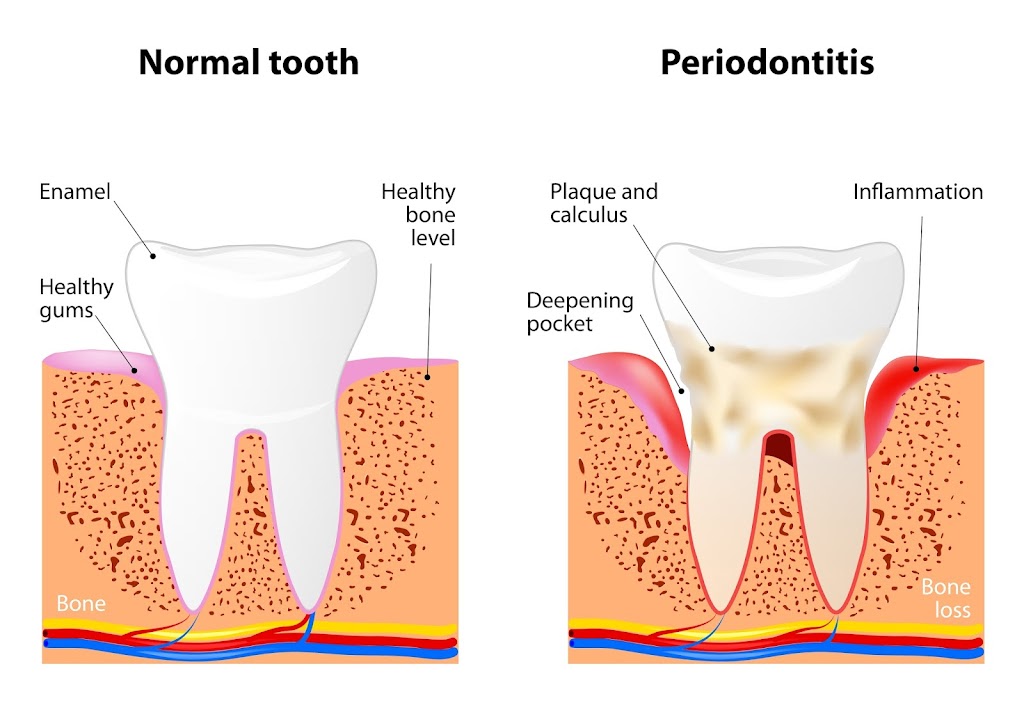
Gingivitis is the most common and least severe form of gum disease, but it’s the first stage of periodontitis. Gingivitis causes bright red and swollen gums that may bleed when brushing or flossing. Often, people don’t see bleeding gums as a problem and continue to neglect dental health. Regular dental exams and dental cleanings performed by a dental hygienist are essential for detecting and managing gum disease early. Gingivitis, although serious, doesn’t always progress to cause tooth loss or other damage.
Plaque buildup is a major risk factor for gum disease. Practicing routine oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth and flossing daily, helps prevent gum disease by controlling plaque and bacteria. After discussing the symptoms of gingivitis, it’s important to note that healthy gums do not bleed and are firm and pink.
Preventing gum disease and taking steps to prevent gum disease through regular care and professional check-ups is crucial in stopping the progression from gingivitis to periodontitis.
Periodontitis, on the other hand, is advanced gum disease and is much more severe. At this stage, the gums recede from the teeth and bone. Deep pockets form within the mouth, trapping bacteria and food debris. These pockets become infected in many cases, filling with bacteria and causing the gum and bone to further dissolve. Identifying risk factors and addressing them early can help prevent severe gum disease. If the jaw structure become too far degraded, reconstructive surgery may be needed.
Periodontitis is a common cause of tooth loss in adults. The infected pockets can cause the teeth to die or rot in most cases, leaving behind odor and pain. Oral operation may be the only option to safely remove the dead tissue.
Is Gum Disease Contagious? The Hidden Risks
When it comes to periodontal disease, many people wonder if it’s something you can “catch” from someone else. While periodontal diseases aren’t contagious in the same way as a cold or the flu, there are hidden risks you should know about. The real culprit behind gum disease is oral bacteria, which thrive in the mouth and can be passed from person to person through saliva.
This means that everyday actions like sharing eating utensils, drinking from the same glass, or even kissing can transfer these bacteria between individuals. If someone in your household has untreated gum disease, the risk of spreading these bacteria increases, especially among family members or partners. Children can also be exposed to these bacteria from parents or caregivers, which may impact their gum health as they grow.
The good news is that you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Practicing good oral hygiene—brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using antibacterial mouthwash—helps remove plaque and reduce the risk of infection. Regular dental exams and professional cleanings are also essential for catching early symptoms of gum disease and keeping your teeth and gums healthy.
Being aware of how periodontal disease bacteria can spread empowers you to make smart choices for your oral health and the well-being of those around you. If you notice warning signs like bleeding gums, swollen gums, or persistent bad breath, don’t wait—schedule a visit with your dental professional to treat gum disease before it becomes a bigger problem.
Avoid Oral Health Risks Caused by Gum Disease
Tooth loss and oral infections are serious problems, but they’re not the only issues that gum disease causes. Studies have linked periodontitis to illnesses and diseases in other areas of the body as well. Untreated gum disease can contribute to serious health problems throughout the body. Improper dental care can lead to:
- Diabetes. Substandard dental health causes inflammation in the mouth that can spread easily. This increased swelling can be associated with diabetes. Periodontitis can not only cause problems, but also exacerbate existing symptoms in someone who is already diabetic. Gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels and may weaken the immune system, making infections more likely.
- Erectile dysfunction. More than half of the men diagnosed with periodontitis also suffered from erectile dysfunction. The exact cause of how gum disease contributes to erectile dysfunction is unknown. However, researchers believe that inflammation and infections are to blame.
- Pneumonia. People with gum disease inhale harmful bacteria each time they take a breath. Over time, this can cause respiratory distress and infections.
Research has also shown links between gum disease and heart disease, including coronary artery disease, as well as other serious conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Taking care of your gums and teeth helps maintain your entire body. Remember to always brush and floss and make regular appointments for evaluations and care. It’s important to have gum disease treated early to prevent further complications.
If you do suffer from tooth loss because of gum disease, Solace implant center & Oral Surgery is here to help. Contact us at 615-320-1392